Configuring guardrails
Guardrails are customizable constraints that enforce safe and compliant agent behavior. They set limits on user inputs and agent responses to prevent inappropriate, insecure, or non-compliant outputs.
Anytime an agent input or response triggers a guardrail during testing, the trace shows information about the policy, what triggered the guardrail, and the action the agent took to block the input or response. Refer to Troubleshooting and debugging agents for more information.
Default guardrails
All agents created in the Agent Designer include the following default guardrails:
- Profanity detection - prevents vulgar or offensive responses
- Prompt attack prevention - Detects and blocks attempts to manipulate agent behavior and its guardrails through adversarial prompts
- General harmful content categories - blocks categories such as hate speech, violence, self-harm, and sexual content
Configurable guardrails
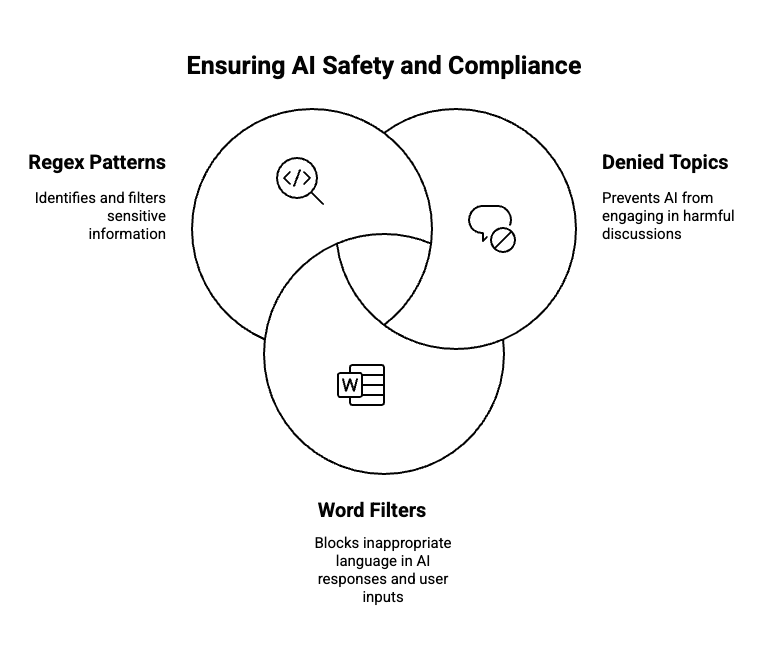
You can configure the following guardrails to apply additional safety mechanisms beyond default settings, such as preventing legal discussions:
| Guardrail type | Definition | Limitations | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Denied topics | Topics that the agent is explicitly prohibited from discussing or responding to, usually for reasons of safety, compliance, or policy. |
| Name: Medical Diagnosis Definition: Requests for identifying or evaluating symptoms, suggesting medical conditions, or recommending specific treatments. Sample phrases: “I have a rash and fever—what could it be?”, “Do I need antibiotics for a sore throat?”, “Can you tell if this mole is cancerous? Name: Investment Advice Definition: Inquiries, guidance, or recommendations about the management or allocation of funds or assets with the goal of generating return or achieving specific financial objectives. Sample phrases: Should I invest in gold? Is investing in stocks better than bonds?” |
| Word filters | Lists of blocked words or phrases that trigger response or input rejection. When detected, the agent returns a predefined blocked message instead of processing the content. Common uses include filtering competitor names or restricted sales language. |
| "lawsuit", "legal advice", "sue", "Can I be arrested", "is it illegal", "statue of limitations", "law". |
| Regex patterns | Custom text-matching rules used to detect and block sensitive data (e.g., credit card or SSN formats) in user inputs or agent responses. Enables precise content filtering using pattern-based guardrails. |
| Email addresses: ^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$ Social security numbers: ^\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}$ |
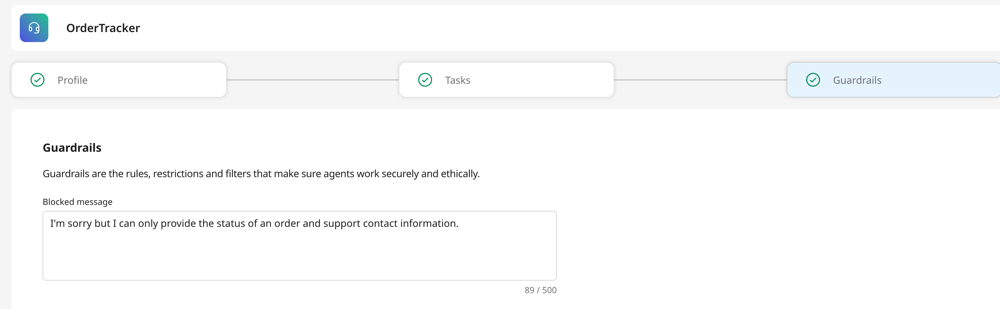
Blocked message
You need to configure a blocked message that the agent will display whenever a guardrail is triggered. For instance, a suitable blocked message could be: "I'm sorry, but I can only provide the status of an order and support contact information."
Blocked messages are intended to inform the user about the limitations of the system without revealing specific words or phrases that triggered the block, preventing the user from circumventing policies by adjusting their approach.
How are guardrails implemented?
Guardrails are processed in parallel to minimize latency. All guardrail policies are applied to both the user’s input text and the agent’s generated responses.
For Denied topics, the Large Language Model (LLM) analyzes the user’s input to check for prohibited subjects. It generates a confidence score based on this analysis. If the confidence score is above 80%, the system replies with a Blocked Message.
