Boomi Agent Designer overview
Boomi Agent Designer is a visual, no-code/low-code, user-friendly interface within Agentstudio for creating goal-driven generative AI agents that automate complex, repeatable processes using natural language prompts and external resources such as APIs, Boomi integrations, and DataHub repositories.
Through Amazon Bedrock, it leverages a framework that selects the best models for specific functions like reasoning, summarization, and guardrails powered by large language models (LLMs). In addition to built-in guardrails, developers can apply custom safety mechanisms to ensure responsible and effective automation. The Agent Designer lets you test your agent iteratively using the Test Agent environment on the right side of your agent configuration.
AI agents built in the Agent Designer are goal-oriented, multi-step applications that use reason and context to take action and complete tasks independently. Create an AI agent to automate a repeatable process that benefits from a non-deterministic approach using an AI-powered assistant.
For examples of AI agents:
-
Explore the AI agent template gallery on the Agent Garden home page for ready-to-deploy and configurable agents you can import. These templates are built by Boomi, Technology Partners, and the Boomi Community.
-
Explore agent examples for step-by-step tutorials, including how to use Agent step and MCP with agents.

Benefits
Agent Designer benefits your organization by:
- Accelerating AI agent deployment with an intuitive, low-code interface
- Supporting scalable, reusable agent designs through YAML-based sharing
- Ensuring safe AI interactions with built-in and customizable guardrails
How do I access Agent Designer?
Navigate to the AI icon in the platform, then click Agent Garden to access the Agent Designer, Agents, and Tools screens.
Agent Designer is included in the Agentstudio Base edition, which is part of all Boomi Enterprise Platform editions.
You receive a notification when you reach usage limitations. To expand usage or add additional capabilities and functionality, contact your Boomi account representative.
Key components
Agents built with the Agent Designer have several components that guide their behavior and functionality.
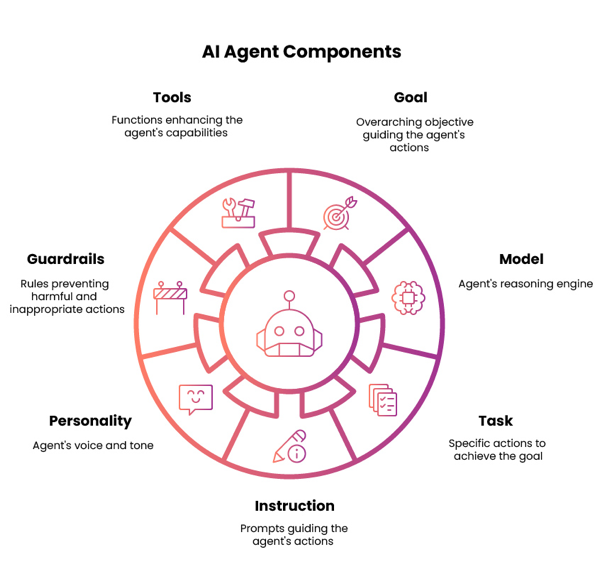
- Goal—The agent goal is a high-level statement that defines the agent's overall purpose/objective. It provides context and boundaries for how the agent should behave and what tasks it will support. For example, "Help users retrieve order statuses and create support tickets."
- Model - A Large Language Model (LLM) powers an agent's reasoning, allowing it to understand natural language inputs, determine intent and context, and generate output in natural language.
- Task - Tasks are functional units of work or specific actions the agent performs to achieve its primary goal. A task can have one or more tools attached to it. For example, "Fetch pending orders."
- Instructions - Instructions are natural language prompts that guide the Large Language Model (LLM) to achieve a task. It influences how the agent interprets user inputs, how the agent responds, and how the agent behaves when performing a task. Instructions can support conditional logic ("if the user does this, do this") and can prevent unwanted behaviors and responses ("do not do this"). For example, "If the user cannot provide an order ID, offer to search orders by first and last name."
- Personality - Personality settings control the agent's voice, tone, and response style.
- Guardrails - Guardrails are filters and controls that manage agent behavior. It prevents unsafe and off-topic responses to ensure an agent performs within your rules and guidelines. Guardrails allow you to define topics you prohibit the agent from discussing and define text and regex filters that trigger and prevent the agent from responding.
- Tools - Tools are functions the agent invokes to help it achieve results related to a task. For example, an agent could use an API tool to call an API endpoint and retrieve an order status. Refer to Adding capabilities to AI agents to learn about the different tool types available.
MCP (Model Context Protocol) support
Create agents that can discover and invoke external tools using MCP, enabling seamless integration, consistent interoperability, and scalable automation across diverse systems. Explore Using MCP to learn more.
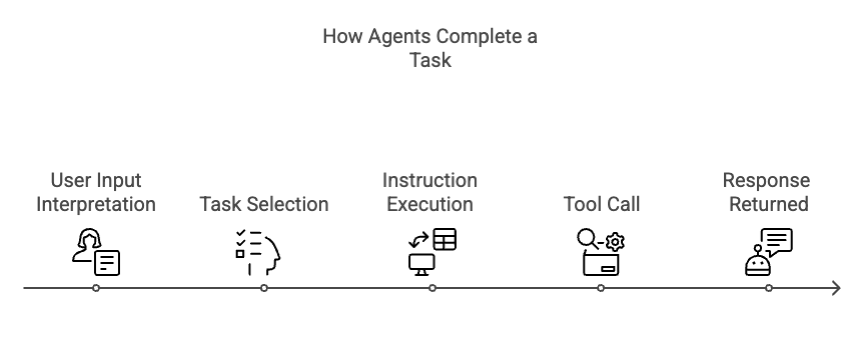
How agents complete a task
The LLM's reasoning determines how and when to initiate a task, execute instructions, and utilize tools. Tools can be shared across tasks, and you can attach the same tool to multiple tasks and instructions. The LLM retains information about user inputs and tool responses and can use that data to execute additional instructions.
Read Building AI agents and Guidelines for building effective AI agents to learn more.
Agent modes
When building an agent, you can choose how an AI agent responds in the Profile screen. There are two agent response modes:
-
Conversational mode (default) - The AI agent responds in natural language text. This mode is ideal for conversational agents where the user may have follow up questions after the initial prompt. The agent can use chat history and context to respond to the user and achieve its goal.
-
Structured mode - The AI agent receives JSON input from Boomi Integration and responds in a consistent, structured JSON format. This model is ideal for workflows that use Agent Step where the agent’s response is consumed by downstream systems. The response is single turn, meaning the agent has a single input and output with no reference to previous responses.
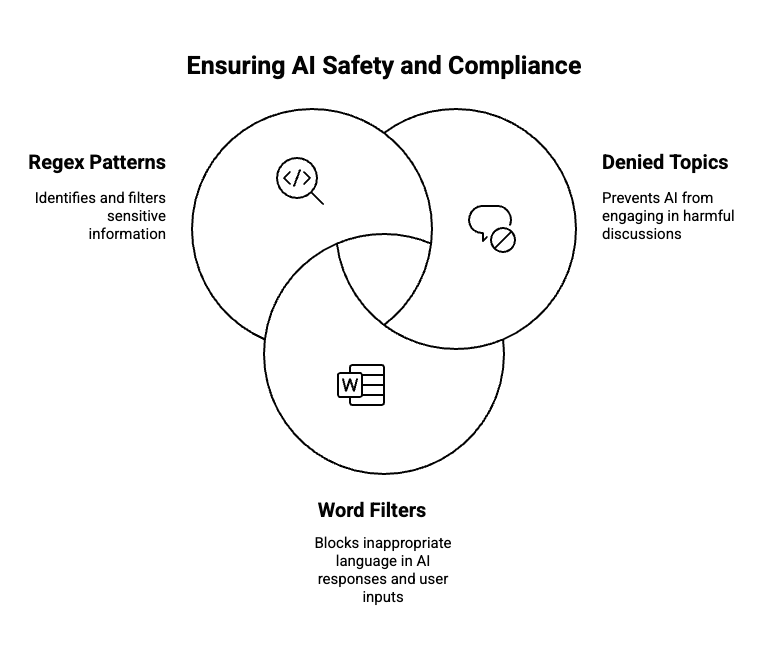
Safety mechanisms
Guardrails are configurable safety controls that govern what an AI agent can say or do, ensuring responsible, secure, and compliant communication. All agents include default protections such as profanity detection, prompt attack prevention, and blocking of harmful content.
Developers can extend these controls by configuring denied topics, word filters, and regex patterns to prevent specific phrases, subjects, or sensitive data from being processed or returned. When a guardrail is triggered, the agent responds with a customizable blocked message without revealing which input caused the restriction.
Read Creating guardrails to learn more.
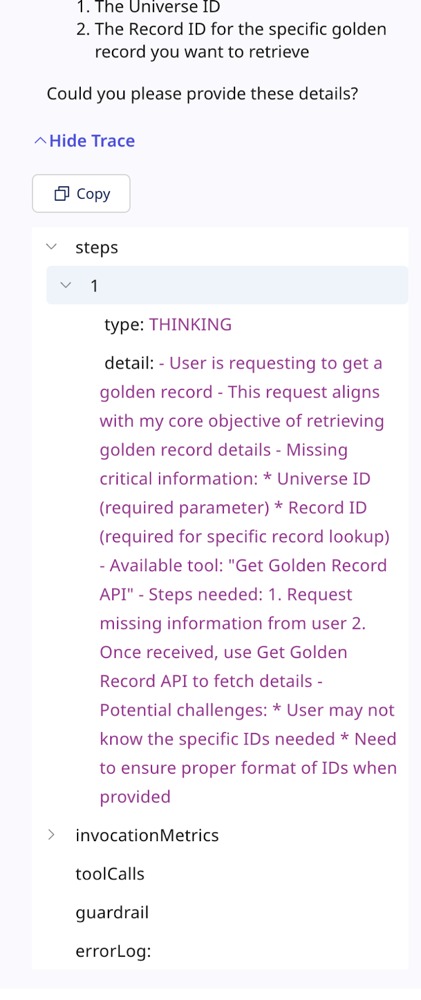
Testing, debugging, and deployment
Before deploying an agent, you can test it in the Test Agent window to validate its behavior and troubleshoot any issues. The agent's responses include a detailed trace showing reasoning, tool usage, and guardrail enforcement, helping you fine-tune tasks, instructions, and configurations. Test your agent to identify issues, monitor LLM invocation metrics, and resolve problems.
Note that testing activity may count toward your usage limits. Once the agent is performing as expected, you can deploy it to make it available to users in the Agent Garden and through the Agent step in an Integration process.
Read Building AI agents and Testing and debugging agents to learn more.